
As time goes by, digital commerce and remote contracting become normalized, but sometimes the user has doubts about the validity of the electronic signature. Even more so when you are aware that there are simple, advanced and qualified ones. Some companies offering remote services and products also have the same questions. What are the answers? The short one is: simple, advanced and qualified electronic signatures that follow the characteristics marked in EU Regulation 910/2014 eIDAS are valid. But each of them has its own use and its capacity in court.. This is part of the long answer that you can read below.
Will you join us?
Electronic and digital signature. Are they the same?
No, they are not the same, even though they are terms that are sometimes interchanged and may seem synonymous.
The electronic signature is a legal concept of acceptance of content, whose main purpose is to attest to the signatory’s will. Regulation (EU) 910/2014, known as eIDAS, defines electronic signatures in its three varieties: simple, advanced and qualified.
A digital signature is a cryptographic mechanism, an encryption and decryption technique that modifies the data in a document to make it unintelligible to an unauthorized recipient. It is part of the advanced and qualified electronic signature, and guarantees the integrity of the data and the identity of the issuer. By means of the digital signature, in addition, the sender cannot deny that he has sent the signed message.
There is a third concept that sometimes appears: digitized signature. The definition in this case is simple. It is the trace of a handwritten signature converted into an image after scanning it or making it on a touch screen. It is therefore equivalent to a simple electronic signature.
The eIDAS regulation defines the common characteristics of the different electronic signatures for all European Union countries. This regulation came to build a space of trust around digital relations (transactions and e-commerce) between member states. Two important features of this regulation are that, on the one hand, it standardizes the experience, the rights of users and the obligations of companies, wherever they are located within the Union’s territory. On the other hand, its content has not had to be transposed, but has been applied directly in all EU countries. Faster and less subject to interpretation.
Types of electronic signature: simple, advanced and qualified.
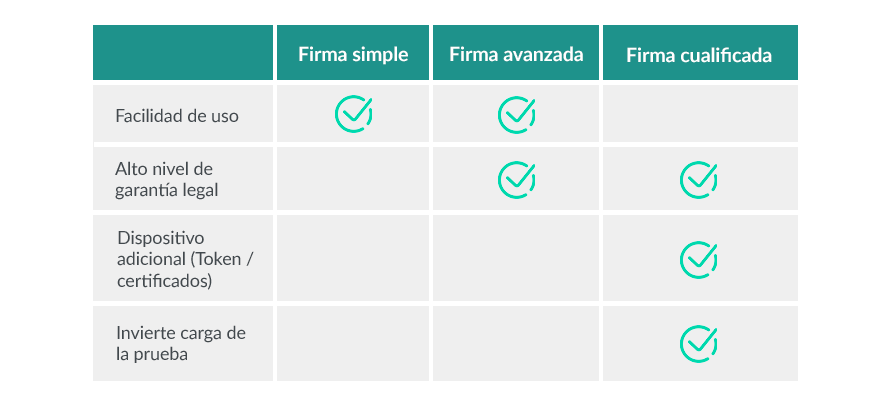
The eIDAS regulation differentiates between three types of electronic signatures according to their security levels, capacity to guarantee the integrity of the signed content and guarantee the identification of the signatory.

2.1 Simple electronic signature
This is the easiest way for a user to sign digitally. As such, it has its advantages and disadvantages. Among the first is the speed of implementation in any process and system. It could be, for example, a simple click on a web page. On the other hand, this system makes it impossible to identify the signatory unequivocally, so it is only suitable for issues with a low legal risk. A quick example is the checkbox to accept general terms and conditions when purchasing a concert ticket.

2.2 Advanced electronic signature
The eIDAS regulation states: “the electronic signature that meets the requirements referred to in Article 26”. And these requirements are, in brief: it must be uniquely linked to the signatory and allow his or her identification. In addition, it must “have been created using electronic signature creation data that the signatory can use, with a high level of confidence, under his exclusive control” and, finally, it must be protected against subsequent modifications. Any changes that occur after signing must be detectable.
The ability of this system to prove that the signer is who he/she says he/she is is very high. And its level of security and integrity as well, but it has to be demonstrated through elements such as, for example, time stamps or evidence that must also be securely guarded.
The advanced signature is combined with digital identification and authentication systems to meet the first of the conditions set by eIDAS. Its implementation is recommended for complex signature processes or with the need for a broad legal guarantee. Among the main advantages that we can offer at Customer Comms for the companies that entrust us with their advanced signature processes are the following:
- Security
- High conversion rate: we generate confidence in the signer thanks to the design of a customized signature process that respects the company’s branding at all times. This translates into a reduction of abandonment rates in the hiring process.
- Ability to integrate the signature in any type of process, to seek the best experience for the user.
- Efficiency and productivity for the company and for the signatory
- Cost reduction
- More agile and customized contracting processes.
- Guaranteed regulatory compliance
- Guarantee of inviolability and integrity of signed documents and collection of evidence.

2.3 Qualified signature
“A qualified electronic signature shall have a legal effect equivalent to that of a handwritten signature.” And if it is based “on a qualified certificate issued in one Member State it shall be recognized as a qualified electronic signature in all other Member States”. This is what eIDAS points out in its article 25.
This type of electronic signature has, therefore, the highest legal guarantees and even reverses the burden of proof. A qualified certificate and a qualified signature creation device, in addition to the systems that assume the characteristics required for the advanced electronic signature, must participate in its realization.
The legal level of the qualified signature is the highest, but also its technical complexity and its integration in the companies’ systems and signature processes. This system is widely used, for example, in the signatories’ relations with public administrations or, in a case recognized by all, with the Tax Agency. But these are not unique use cases, far from it, and some platforms, like ours, offer it for cases where extreme legal certainty is necessary.
3. Electronic signature: choosing a supplier
The implementation of an electronic signature solution is one of the most relevant steps to achieve success in the digital transition process in the company. That is why it is important to choose a provider that allows you to securely integrate into your systems a tool that adapts to the different levels of electronic signature for contracts with employees, customers and suppliers.
At Customer Comms we provide companies with a complete signature solution that adapts to the needs of each business process. This solution is based on proprietary technology, our CertySign platform, and complements and orchestrates third-party technologies to build the most appropriate signature ceremony in each case.
Our solution allows you to launch, trace, certify and safeguard simple, advanced or qualified signature processes, complementing them with identity verification and authentication processes that make them even more robust. And it does so with agility in its implementation, cost savings, optimization of the user experience, paper reduction and greater security in both legal and error minimization.
This platform, called CertySign, combines several aspects: that of
compliance
compliance, with an eye on the eIDAS regulation, legal assurance as a qualified electronic trust service provider, and user experience (whether for customers, suppliers or employees) are three of them.
4. Innovation: Virtual Signature Room.
Electronic signature of documents with “human factor

Our Virtual Signature Room is an innovative platform that allows you to include the human factor in the remote signing of complex agreements, through guided and secure videoconference sessions in which signatories and professionals from your company participate, with the possibility of advising in real time. The electronic signature modality chosen by each company is perfectly integrated into the session, as well as the identification and authentication system of the people who have to sign.
The use of this platform is especially indicated for the signing of agreements in which personalized advice, or the participation of third parties, is necessary or convenient. For example, in home sales and purchases, mortgage loans, complex insurance policies or agreements in which lawyers are also involved.
The Virtual Signature Room offers a new concept of user experience for this type of complex operations, which translates into high levels of completion, and which we offer through our partner OneSpan.